The role of Critical Technologies in accelerating global agrifood trade
As global food systems grow increasingly complex and interconnected, the demand for secure, transparent, and efficient trade mechanisms is rising. In this context, blockchain has evolved beyond a single-use technology to become a strategic innovation platform, enabling a new wave of transformation in agrifood trade. Within this platform, critical technologies—from smart contracts to decentralized finance (DeFi), digital identity, and tokenized assets—are redefining how value is created, exchanged, and trusted across supply chains.
This article explores how blockchain, as a foundation for multiple decentralized technologies, accelerates the shift toward more agile, fair, and transparent global agrifood commerce.
A converging platform for trade, trust, and transparency
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a distributed network. But its real power lies in the ecosystem of technologies it enables. These include:
- Smart contracts: Self-executing agreements that automate transactions under predefined conditions
- Digital wallets: Tools that store and transfer digital assets securely
- Cryptocurrencies and stablecoins: Mechanisms for seamless, cross-border payments
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): Financial services without traditional intermediaries
- Food-specific blockchains: Systems designed to capture and verify data in agrifood supply chains
- Identity frameworks: Digital IDs that ensure transparency and traceability
- Marketplaces: Peer-to-peer platforms for commodity exchange
Together, these elements form an infrastructure that brings different and essential capabilities to agrifood trade like decentralization – reduces reliance on centralized authorities of intermediaries – immutability – prevents tampering and ensures data integrity – transparency – enables traceability and real-time verification across the value chain.
Disrupting traditional models: From intermediated to peer-to-peer trade
Conventional agrifood trade relies heavily on intermediaries to verify, finance, and execute transactions. While this adds a layer of control, it also increases complexity, cost, and time. Blockchain-enabled systems are transforming this model by making direct, peer-to-peer trade viable—without compromising on trust or compliance.
With the support of smart contracts and digital identities, producers and buyers can transact directly, ensuring faster payments, automated documentation, and real-time quality control. Early market analyses suggest that this disintermediation can increase value capture for producers by 10–20%, while also improving access to capital and global markets.
Use cases: How the platform is being deployed today
Leading companies and innovators are already using blockchain-based platforms to unlock efficiency and transparency in agrifood supply chains:
- Maersk uses IoT sensors in refrigerated containers to record temperature and humidity data on blockchain-based smart contracts, ensuring cold chain integrity during transit.
- Agrotoken enables farmers to tokenize their grain and use it as digital collateral for transactions or financing, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries and expanding access to capital.
These examples showcase how blockchain can serve as the infrastructure for real-time, trusted, and data-driven agri-food trade.
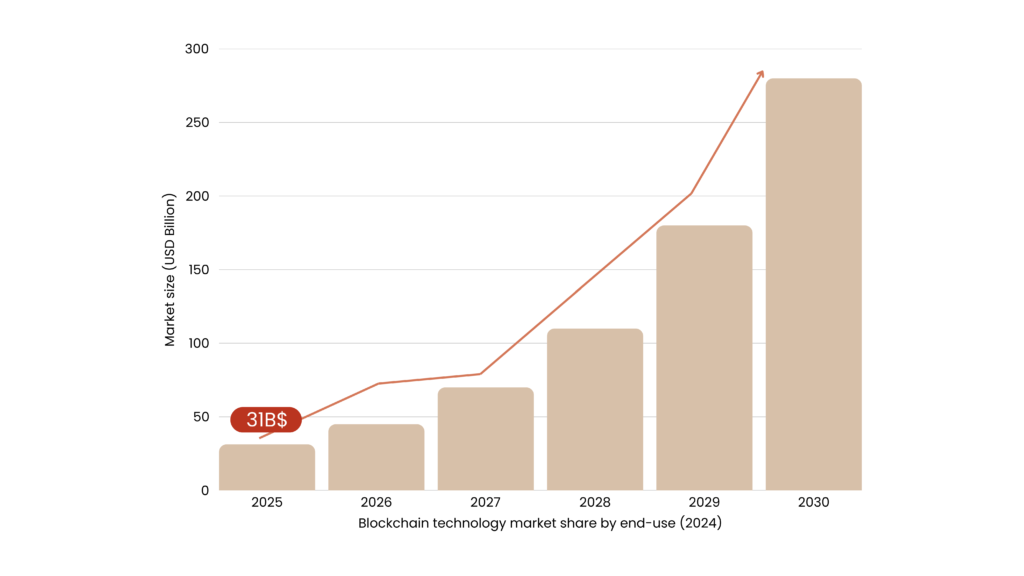
A rapidly scaling market
The blockchain market is growing at unprecedented speed. Estimates suggest it will reach between $31 and $50 billion by 2025, with a projected CAGR of up to 90% through 2030. While initial growth has been concentrated in finance and logistics, the agrifood sector is emerging as a strategic frontier, especially in applications involving traceability, automation, tokenized assets, and smart contracts.
Source: Grand View Research. Blockchain Technology Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.
This exponential growth is fueled not only by the expansion of public blockchain infrastructure, but also by the rise of hybrid and private blockchain networks, offering flexible solutions for enterprise and industrial use cases. These architectures are especially relevant for sectors like agrifood, where both transparency and controlled access are essential.
By investing in this convergence now, stakeholders in the food value chain can gain early-mover advantages in efficiency, market access, and traceability—while helping shape the infrastructure of decentralized global trade.
Looking ahead: building infrastructure for decentralized trade
To fully realize the potential of blockchain as a platform for agrifood innovation, key challenges remain. Interoperability between systems, regulatory harmonization, and rural digital infrastructure are critical enablers for mainstream adoption. However, the foundations are already in place, and the shift is underway.
The long-term vision is clear: a decentralized trading infrastructure where data replaces paperwork, code replaces intermediaries, and trust is embedded in every transaction. This is not just a technological evolution—it is a systemic rethinking of how food and raw materials move through the global economy.
By embracing blockchain as a strategic platform of innovation, the agrifood sector stands to gain more than just efficiency. It can unlock new forms of value, create more inclusive markets, and build a trade system fit for the future.